Archive for May 2014
PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM (Exploration 1)
 |
| The Pythagoras' Theorem |
The theorem states that the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the remaining sides. That is c^2 = a^2 + b^2, where c is the hypotenuse, a and b are the lengths of the remaining sides.
Here is one of the theorem. Take note that the theorem only applies to right triangles.
Start with a cutout of any right triangle.
Let us name the shortest side as a, the longer side as b and the hypotenuse as c.
Let us make three (3) more of the right triangle.
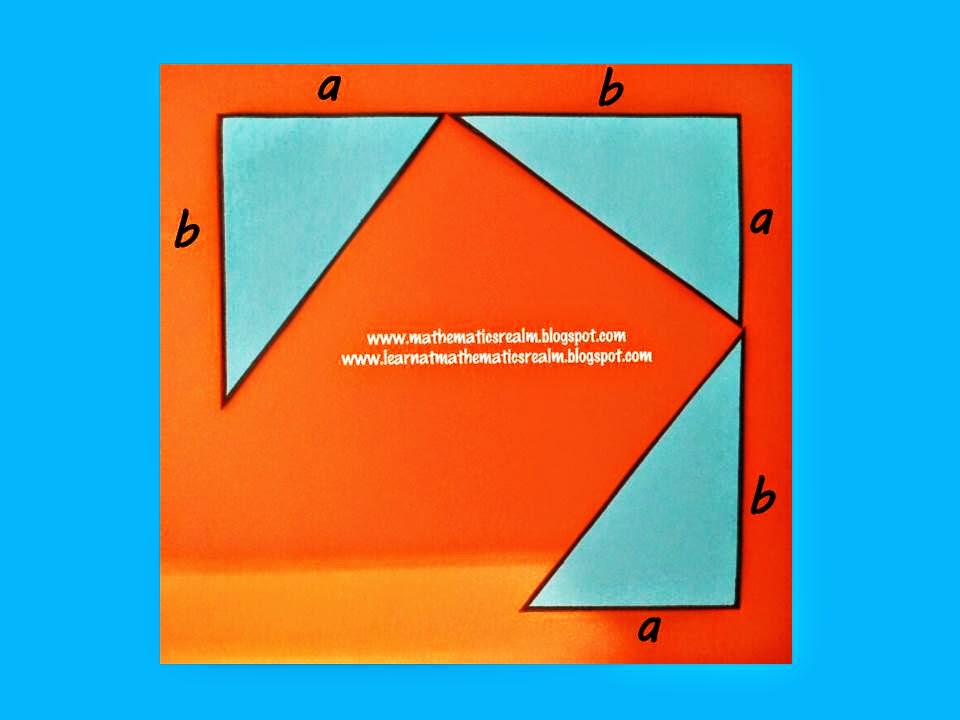
Our next step is to form a square out of the four (4) triangles, making sure that the combined length of a and b will be the length of the side of the square that we are forming.
Let us take a look at the different parts of the square we formed. If we separate the whole square, we can get its area in terms of a and b.
The middle part is also a square with sides equal to the hypotenuse of the right triangle. The area can also be obtained.
The area of the four right triangles outlining the sides of the whole square is as follows
We take note that the area of the whole square is equal to the area of the small square in the middle added to the area of the four right triangles. That is
Thus, c^2 = a^2 + b^2.
Hope this will help you understand the derivation of the Pythagoras' Theorem.
Your comments and suggestions are welcome here. You may write them in the comment box below. Thank you!
Saturday, May 24, 2014